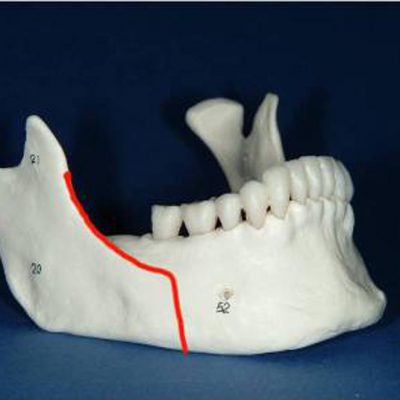
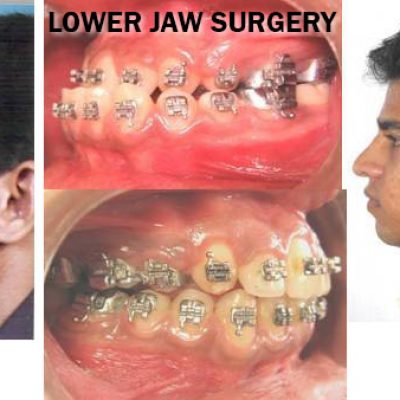
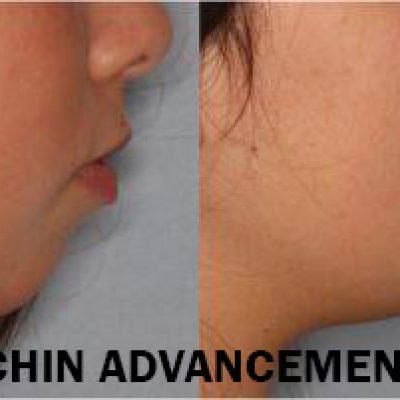
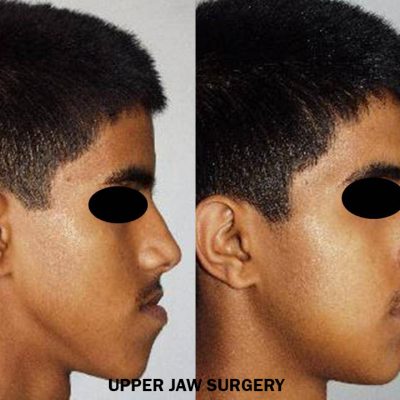
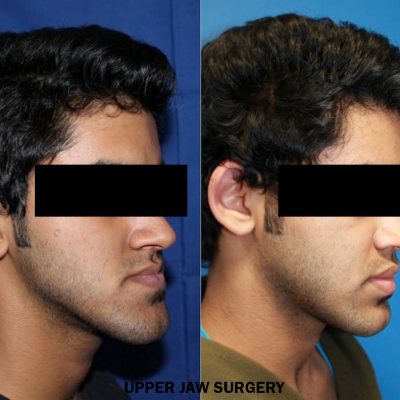
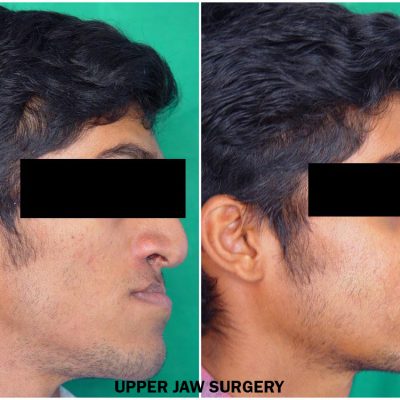
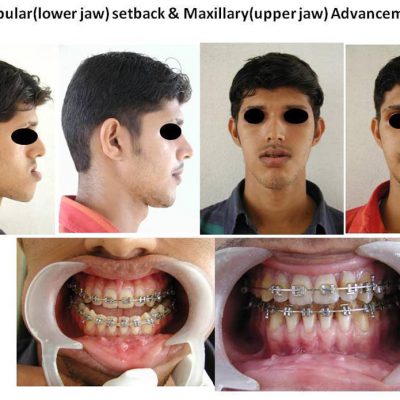
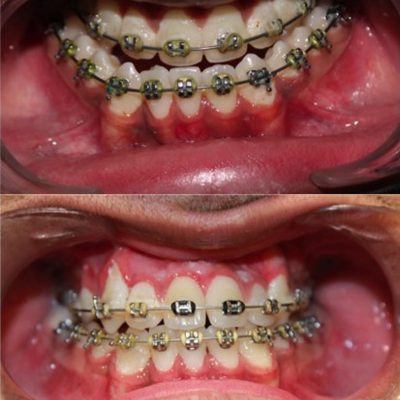
Corrective jaw, or orthognathic, surgery is performed to correct a wide range of minor and major skeletal ( Bony) and dental irregularities, including the misalignment of jaws and teeth. While the patient’s appearance may be dramatically enhanced as a result of their surgery, orthognathic surgery is performed to correct functional problems
Following are some of the conditions that may indicate the need for corrective jaw surgery:
- difficulty chewing, or biting food
- difficulty swallowing
- chronic jaw or jaw joint (TMJ) pain and headache
- gummy smile
- open bite (space between the upper and lower teeth when the mouth is closed)
- unbalanced facial appearance from the front, or side
- post traumatic facial defect correction
- birth defects
- receding chin
- protruding jaw
- inability to make the lips meet without straining
- chronic mouth breathing and dry mouth
- sleep apnea (breathing problems when sleeping, including snoring)
Orthognathic surgery along with improvement in appearance can also improve chewing, speaking and breathing.