ORTHOGANTIC SURGERY AND DISTRACTION
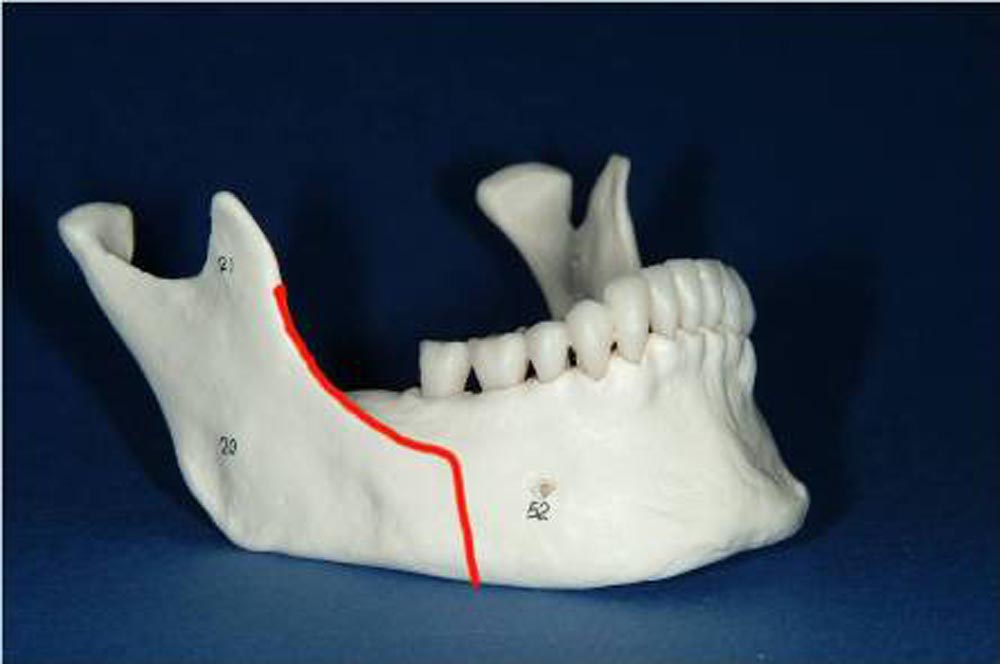

Orthognatic Surgery
Corrective jaw, or orthognathic, surgery is performed to correct a wide range of minor and major skeletal ( Bony) and dental irregularities, including the misalignment of jaws and teeth and treats sleep apnea.
While the patient’s appearance may be dramatically enhanced as a result of their surgery, orthognathic surgery is performed to correct functional problems














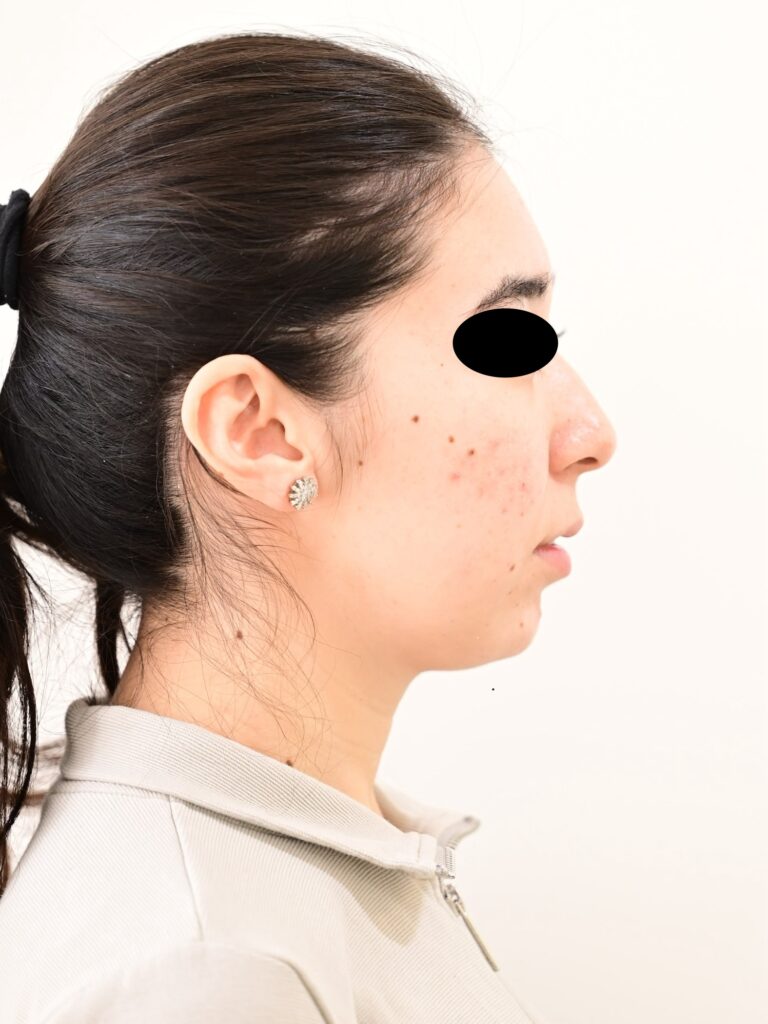
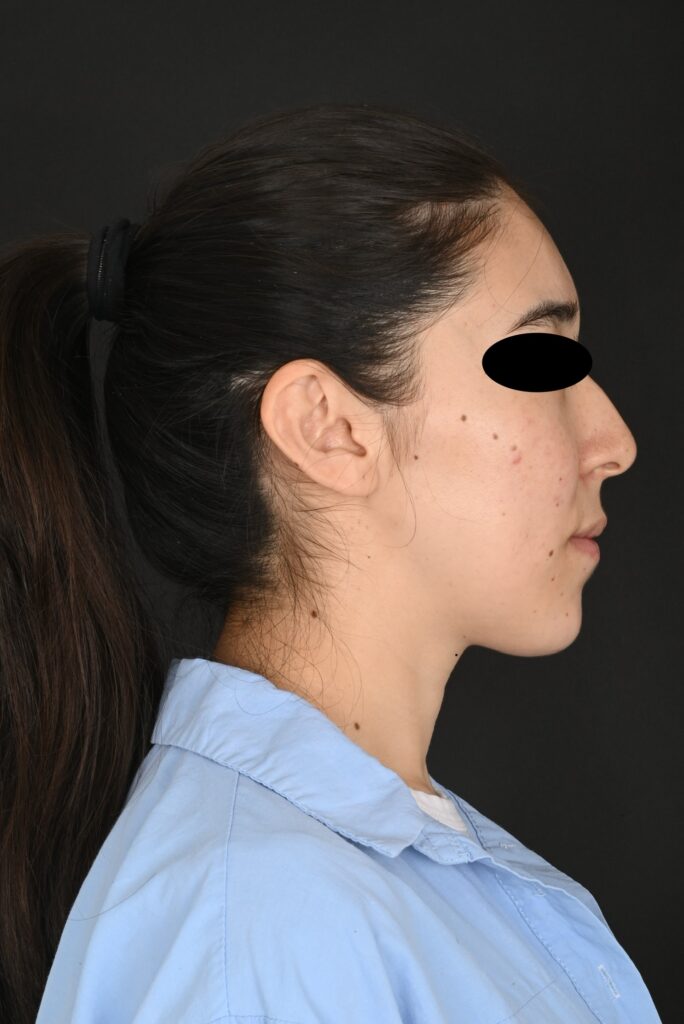
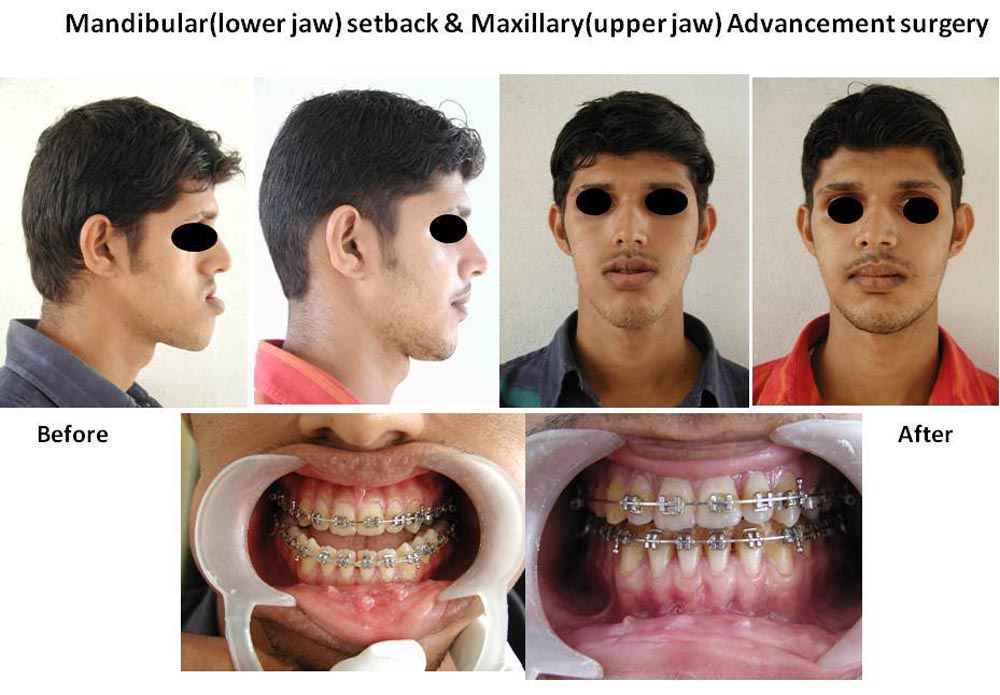
Following are some of the conditions that may indicate the need for corrective jaw surgery:
Orthognathic surgery along with improvement in appearance can also improve chewing, speaking and breathing.
Distraction
Distraction is a surgical process used to reconstruct skeletal deformities and lengthen the bones of the body.
A corticotomy is used to fracture the bone into two segments, and the two bone ends of the bone are gradually moved apart during the distraction phase using a device called the distractor , allowing new bone to form in the gap. These techniques are now utilised extensively by maxillofacial surgeons for the correction of micrognathia (small chin), midface, and fronto-orbital hypoplasia ( deficient midface) in patients with craniofacial deformities.
Intraoral Distractor
An intraoral distractor is a specialized device used to gradually lengthen the jawbone or other facial structures.
In orthognathic surgery, an intraoral distractor is used to gradually lengthen jawbones in cases of micrognathia or after trauma, correcting misalignments through controlled bone movement.

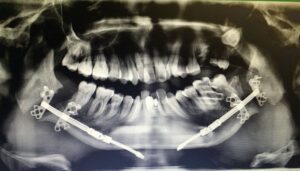
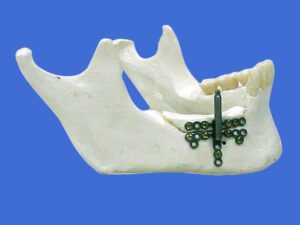
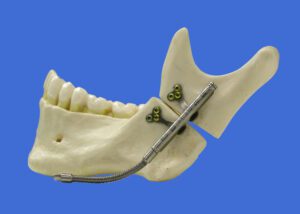





Benefits of Intraoral Distractor:
- Non-Invasive Bone Lengthening – Provides a way to gradually lengthen the jaw without external incisions.
- Customized for Each Patient – The device is tailored to each patient’s needs, ensuring precise results.
- Improves Facial Aesthetics & Function – Enhances both appearance and the ability to chew, speak, and breathe.
- Minimizes Recovery Time – The gradual adjustment reduces trauma to surrounding tissues, promoting faster healing.
Intraoral distractors are a key tool in treating severe jaw discrepancies, offering a less invasive, effective solution for long-term facial and dental health improvement.



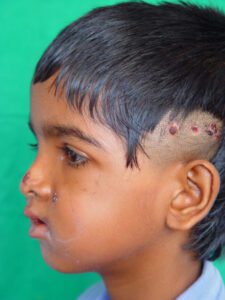

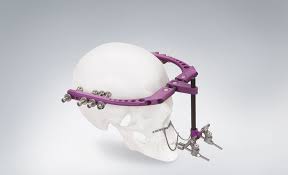
Extraoral Distractor
An extraoral distractor is an external device used to lengthen the jawbone or correct facial skeletal deformities.
Used for complex cases like severe jaw discrepancies or trauma, an extraoral distractor attaches externally to the head, gradually lengthening the bone through pins inserted into the bone.




Benefits of Extraoral Distractor:
- Effective for Severe Deformities – Ideal for complex cases requiring significant bone movement.
- Precise & Controlled Bone Lengthening – Allows gradual and accurate correction of jaw misalignments.
- Improves Facial Function & Aesthetics – Enhances both appearance and the ability to chew, speak, and breathe.
- Minimized Risk of Rejection – The device is externally supported, reducing complications that may arise from internal devices.
Extraoral distractors are highly effective in restoring facial balance and improving functionality for patients with complex facial skeletal issues.
Dr. Gagan Sabharwal's clinic: Delhi
011-45033566
Fakeeh University Hospital, Dubai
+971-44144444
Jumeirah Clinic, Dubai
+1-80037569
